Learning to Reason over Multi-Granularity Knowledge Graph for Zero-Shot Urban Land-Use Mapping
Remote Sensing of Environment
Yansheng Li1, Yu Wang1*, Lei Yu2, Bo Dang1, Gang Xu1, Zhenyu Zhong1, Yuning Wu1, Xin Guo3, Kang Wu1, Zheng Li1, Linlin Wang1, Jian Wang2, Jingdong Chen2, Ming Yang2, Yongjun Zhang1*
Wuhan University1, Ant Group2, Shanghai Academy of AI for Science3
Abstract
Accurate urban land-use mapping is an essential undertaking for various urban issues, such as urban planning, disease transmission, and climate change. Recently, learning-based method has emerged as a prevalent approach for urban land-use mapping, although it relies heavily on abundant labeled data. However, since land-use categories are jointly determined by physical and social attributes, obtaining such labels is challenging. This scarcity of labeled data often leads existing learning-based methods to overfit, resulting in models that struggle to recognize diverse land-use categories. To bypass these limitations, this paper for the first time advocates knowledge graph to leverage indirect supervision from related tasks for zero-shot land-use mapping. Toward this goal, this paper introduces a multi-granularity knowledge graph reasoning (mKGR) framework. Only with indirect supervision from other tasks, mKGR can automatically integrate multimodal geospatial data as varying granularity entities and rich spatial-semantic interaction relationships. Subsequently, mKGR incorporates a fault-tolerant knowledge graph embedding method to establish relationships between geographic units and land-use categories, thereby reasoning land-use mapping outcomes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that mKGR not only outperforms existing zero-shot approaches, but also exceeds those with direct supervision, achieving improvements from 0.08 to 0.20 across several performance metrics. Furthermore, this paper reveals the superiority of mKGR in large-scale holistic reasoning, an essential aspect of land-use mapping. Benefiting from mKGR’s zero-shot classification and large-scale holistic reasoning capabilities, a comprehensive urban land-use map of China is generated with low-cost. In addition, a nationwide assessment of 15-minute city walkability over the land-use map provides insights for urban planning and sustainable development.
Metric
| Dataset | PA | UA | OA | MRR | Hit@1 | Data | Model |
| Wuhan | 43.1 | 44.4 | 71.6 | 85.5 | 78.4 | Zenodo | Zenodo |
| Guangzhou | 56.5 | 49.5 | 79.2 | 82.9 | 74.7 | Zenodo | Zenodo |
| Shanghai | 53.0 | 52.3 | 81.7 | 87.0 | 80.2 | Zenodo | Zenodo |
| Lanzhou | 21.6 | 33.1 | 59.9 | 83.4 | 77.8 | Zenodo | Zenodo |
| Yulin | 30.2 | 35.4 | 63.5 | 77.0 | 68.3 | Zenodo | Zenodo |
| Whole China | 35.6 | 37.9 | 71.1 | – | – | Zenodo | Zenodo |
Visualization

MKG on Wuhan City (12w nodes, 32w links)
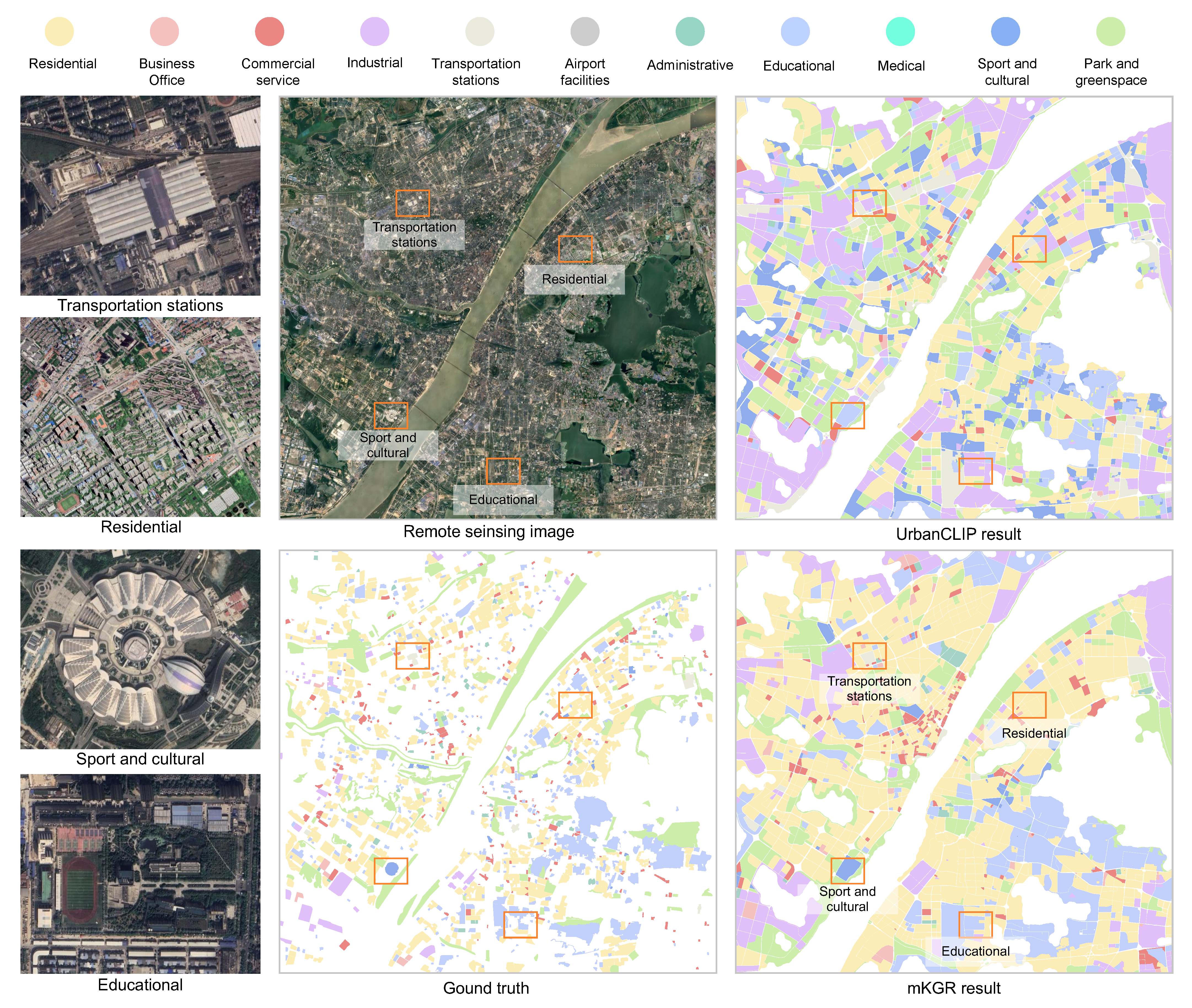
Land-use map of Wuhan City
@article{li2025learning,
title={Learning to reason over multi-granularity knowledge graph for zero-shot urban land-use mapping},
author={Li, Yansheng and Wang, Yu and Yu, Lei and Dang, Bo and Xu, Gang and Zhong, Zhenyu and Wu, Yuning and Guo, Xin and Wu, Kang and Li, Zheng and others},
journal={Remote Sensing of Environment},
volume={330},
pages={114961},
year={2025},
publisher={Elsevier}
}